【SUMMARY】
Gonorrhea and Chlamydia are very common STDs accounting for nearly 45% of all STD cases. A combination testing of the two helps in simultaneous testing for the two most common causative agents of STDs. Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted disease caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. It is most frequently transmitted during sexual intercourse, including vaginal, oral and anal sex. It can infect the throat, producing a severe sore throat, can infect the anus and rectum, producing a condition called proctitis. In females, it can infect the vagina, causing irritation with drainage (vaginitis). Infection of the urethra may cause urethritis with burning, painful urination, and a discharge. When women have symptoms, they often note vaginal discharge, increased urinary frequency, and urinary discomfort. Spread of the organism to the fallopian tubes and abdomen may cause severe lower-abdominal pain and fever. The average incubation for Gonorrhea is approximately 2 to 5 days following sexual contact with an infected partner. However, symptoms may appear as late as 2 weeks. A preliminary diagnosis of Gonorrhea can be made at the time of examination. 1 In women, Gonorrhea is a common cause of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). PID can lead to internal abscesses and long-lasting, chronic pelvic pain. PID can damage the fallopian tubes enough to cause infertility or increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy. 2 Chlamydia trachomatis is the most common cause of sexually transmitted venereal infection in the world. Composed of elementary bodies (the infectious form) and reticulate or inclusions bodies (the replicating form), Chlamydia trachomatis has both a high prevalence and asymptomatic carriage rate, with frequent serious complications in both women and neonates. Complications of Chlamydia infection in women include cervicitis, urethritis, endometritis, PID and increased incidence of ectopic pregnancy and infertility. 3 Vertical transmission of the disease during parturition from mother to neonate can result in inclusion conjunctivitis pneumonia. In men, complications of Chlamydia infection include urethritis and epididymitis. Approximately 70% of women with endocervical infections and up to 50% of men with urethral infections are asymptomatic.
The Gonorrhea and Chlamydia Combo Rapid Test Cassette (Swab) is a rapid test to qualitatively detect the Gonorrhea and Chlamydia antigen from female cervical swab and male urethral swab specimens.
【DIRECTIONS FOR USE 】
Allow the test, reagents, swab specimen, and/or controls to reach room temperature (15- 30 ℃) prior to testing.
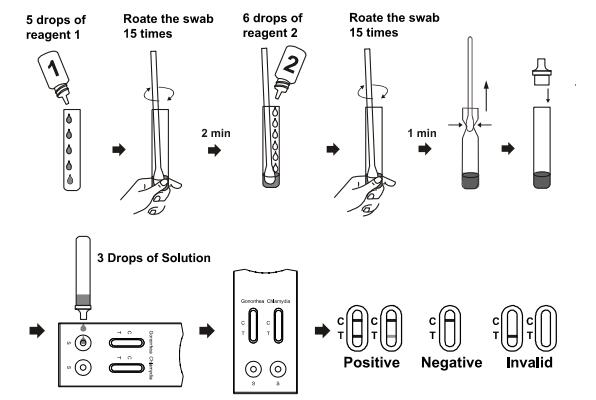
1. Remove the test cassette from the foil pouch and use it within one hour. Best results will be obtained if the test is performed immediately after opening the foil pouch.
2. Extract the Chlamydia antigen according to the specimen type.
For Female Cervical or Male Urethral Swab Specimen:
Hold the reagent 1 bottle vertically and add 5 drops of reagent 1 (approx. 300ul) to the extraction tube. Reagent 1 is colorless. Immediately insert the swab, compress the bottom of tube and rotate swab 15 times. Let stand for 2 minutes.
Hold the reagent 2 bottle vertically add 6 drops of reagent 2 (approx. 250ul) to the extraction tube. The solution would turn turbid. Compress the bottle of tube and rotate the swab 15 times until the solution turn clear with a slight green or blue tint. If the swab is bloody, the color will turn yellow or brown. Let stand 1 minute.
Press the swab against the side of tube and withdraw the swab while squeezing the tube. Keep as much liquid in the tube as possible. Fit the dropper tip on top of extraction tube.
|
Cat. No. |
Product Description |
Specimen |
Format |
Kit Size |
Cut-Off |
Status |
|
IGC-525 |
Gonorrhea and Chlamydia Combo Rapid Test Cassette |
Swab |
Cassette |
10 T |
See Insert |
Non-CE |
 Malaysia
Malaysia