【SUMMARY】
Noroviruses (NoV) are a genetically diverse group of single stranded RNA, nonenvelopped viruses belonging to the Caliciviridae family. For decades they were called “small round structured viruses” (SRSV) or “Norwalk-like viruses” until recently when their taxonomy was investigated using modern molecular techniques. Initially four antigenic types of SRSV were recognized, but more recently three genogroups have been identified with the genus Norovirus.Genogroup 1 and Genogroup 2 are associated with human infections whilst Genogroup 3 is associated with bovine and porcine infection.
Noroviruses are a major cause of acute gastroenteritis worldwide, often causing explosive outbreaks in institutions. They are highly contagious, with an inoculum of as few as ten particles being able to cause infection. Transmission occurs through ingesting contaminated food and water and by person-to-person spread. Transmission is predominantly fecal-oral but may be airborne due to aerosolisation of vomitus, which typically contains abundant infectious virus particles. Outbreaks may involve several routes of transmission. The illness is acute, usually mild, although it has caused fatalities among the frail elderly, and self-limiting and follows an incubation period of 24-48 hours although cases can occur within 12 hours of exposure. The ability of Noroviruses to cause outbreaks in institutions has become a major public health issue. Outbreaks of Norovirus infection can be associated with restaurants and institutions as diverse as nursing homes, hospitals and elite sporting camps. Infections in infants, elderly or frail patients can be fatal if left untreated.
The symptoms of Norovirus illness usually include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and some stomach cramping. Sometimes people additionally have a low-grade fever, chills, headache, muscle aches, and a general sense of tiredness. The illness often begins suddenly, and the infected person may feel very sick. In most people the illness is self-limiting with symptoms lasting for about 1 or 2 days. In general, children experience more vomiting than adults.
【DIRECTIONS FOR USE】
Allow the test, specimen, buffer, and/or controls to reach room temperature (15-30°C) prior to testing.
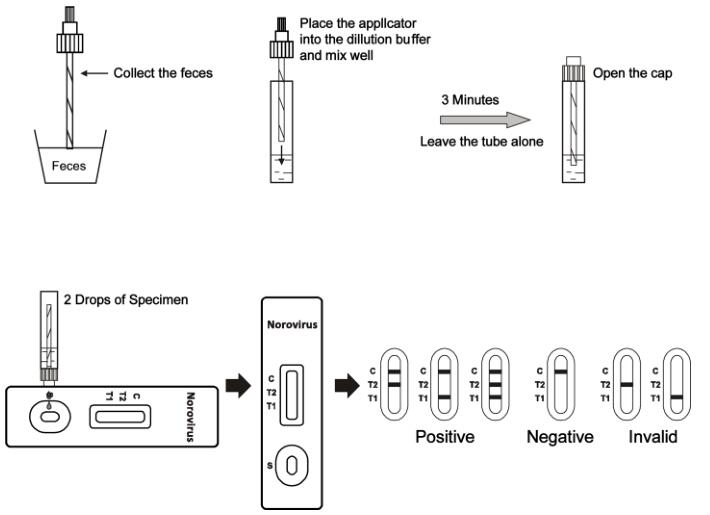
1. To collect fecal specimens:Collect sufficient quantity of feces (1-2 mL or 1-2 g) in a clean, dry specimen collection container to obtain enough virus particles. Best results will be obtained if the assay is performed within 6 hours after collection. Specimen collected may be stored for 3 days at 2-8°C if not tested within 6 hours. For long term storage, specimens should be kept below -20°C.
2. To process fecal specimens:
For Solid Specimens:
Unscrew the cap of the specimen collection tube,then randomly stab the specimen collection applicator into the fecal specimen in at least 3 different sites to collect approximately 50 mg of feces (equivalent to 1/4 of a pea). Do not scoop the fecal specimen.
For Liquid Specimens:
Hold the dropper vertically, aspirate fecal specimens, and then transfer 50µL into the specimen collection tube containing the extraction buffer.
Tighten the cap onto the specimen collection tube, then shake the specimen collection tube vigorously to mix the specimen and the extraction buffer.
3. Bring the pouch to room temperature before opening it. Remove the test cassette from the foil pouch and use it as soon as possible. Best results will be obtained if the test is performed immediately after opening the foil pouch.
4. Hold the specimen collection tube upright and unscrew the small cap of the specimen collection tube. Invert the specimen collection tube and transfer 2 full drops of the extracted specimen (approximately 80µL) to the specimen well (S) of the test cassette, then start the timer. Avoid trapping air bubbles in the specimen well (S). See illustration below.
5. Read the results at 15 minutes after dispensing the specimen. Do not read results after 20 minutes.
Note: If the specimen does not migrate (presence of particles), centrifuge the diluted sample contained in the extraction buffer vial. Collect 80 µL of supernatant, dispense into the specimen well (S). Start the timer and continue from step 5 onwards in the above instructions for use.
|
Cat. No. |
Product Description |
Specimen |
Format |
Kit Size |
Cut-Off |
Status |
|
INO-602 |
Norovirus Rapid Test Cassette |
Feces |
Cassette |
10 T |
See Insert |
CE |
 Malaysia
Malaysia