Description
【SUMMARY】
Streptococcus pneumoniae, or pneumococcus, is a Gram-positive, alpha-hemolytic (under aerobic conditions) or beta-hemolytic (under anaerobic
conditions), facultative anaerobic member of the genus Streptococcus,1 As a
significant human pathogenic bacterium S. pneumoniae was recognized as a
major cause of pneumonia in the late 19th century, and is the subject of many humoral immunity studies. S. pneumoniae resides asymptomatically in healthy carriers typically colonizing the respiratory tract, sinuses, and nasal cavity.
However, in susceptible individuals with weaker immune systems, such as the
elderly and young children, the bacterium may become pathogenic and spread to other locations to cause disease. It spreads by direct person-to-person contact via respiratory droplets and by autoinoculation in persons carrying the bacteria in their upper respiratory tract.2
It can be a cause of neonatal infections.3 S. pneumoniae is the main cause of community acquired pneumonia and meningitis in children and the elderly,4
and of septicemia in those infected with HIV. The organism also causes many types of pneumococcal infections other than pneumonia. These invasive pneumococcal diseases include bronchitis, rhinitis, otitis media, conjunctivitis, meningitis, sepsis,osteomyelitis, septic arthritis, endocarditis, peritonitis, pericarditis, cellulitis, and brain abscess.5
Legionellosis is a serious pneumonia caused by bacteria of the genus Legionella assigned to the family Legionellaceae. This family now includes 48 species and over 60 serogroups. Approximately 20 species are implicated in human disease. The overwhelming majority of Legionella infections are caused by Legionella pneumophila. Legionnaires' disease is the major clinical manifestation of Legionella infection although extra-pulmonary infection and non-pneumonic disease like Pontiac fever occur. Legionella pneumophila is responsible for approximately 90% of infections, and of these, over 80% are due to a single serogroup, serogroup.
Legionnaires' disease (LD) is not contagious. The disease is transmitted by aerosol, and there is no evidence for direct person-to-person transmission. Person at risk are those whose immune system is compromised, including transplant recipients, the elderly, cigarette smokers, or those showing chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or chronic renal disease.
【DIRECTIONS FOR USE】
Allow the test, specimen and/or controls to reach room temperature
(15-30°C) prior to testing.
1. Remove the test cassette from the foil pouch and use it within one hour. Best results will be obtained if the test is performed immediately after opening the foil pouch.
2. Place the cassette on a clean and level surface.
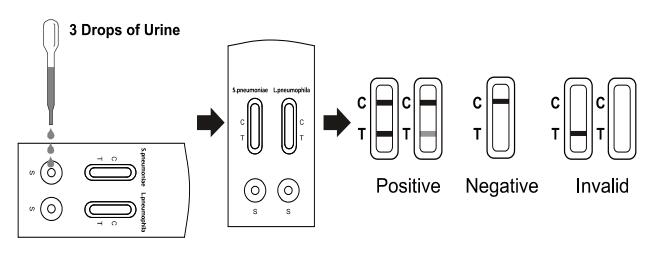
3. Absorb the urine specimen with a dropper, add 3 full drops (approx.120ul)
specimen into the sample well (S) of test cassette vertically.
4. Wait for the colored line(s) to appear. Read results at 15 minutes. Do not
interpret the result after 20 minutes.
|
Cat. No.
|
Product Description
|
Specimen
|
Format
|
Kit Size
|
Cut-Off
|
Status
|
|
ISLC-125
|
Legionella pneumophila and Streptococcus pneumoniae Rapid Test Cassette
|
Urine
|
Cassette
|
10 T
|
See Insert
|
CE
|
More detail about Setia Scientific Solution
 Malaysia
Malaysia