Description
Keloid and hypertrophic scars are two types of scars that can form as a result of injury, surgery, or inflammation. While they may look similar, there are some differences between these two types of scars, and the treatment approaches may vary.
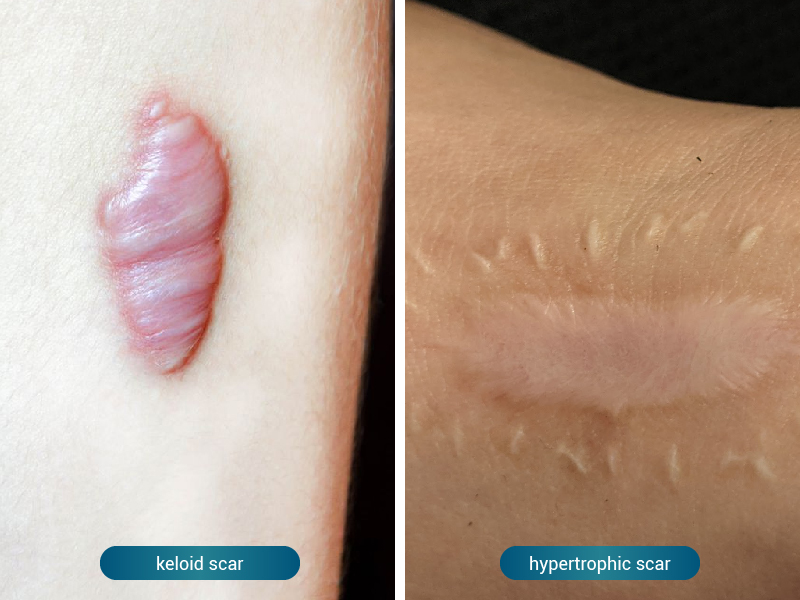
Keloid scars:
-
Keloids are raised, thickened, and often have a smooth and shiny surface.
-
They can extend beyond the borders of the original wound and grow indefinitely.
-
Keloids are more common in people with darker skin types and can be itchy, painful, or even restrict movement if they grow large enough.
-
Treatment options for keloids may include corticosteroid injections, surgical removal, laser therapy, cryotherapy, and radiation therapy. However, keloids have a tendency to recur, so the treatment may need to be repeated.
Hypertrophic scars:
-
Hypertrophic scars are raised and thickened but typically do not extend beyond the borders of the original wound.
-
They tend to be red and may be itchy or painful.
-
Hypertrophic scars usually develop within the first few months after an injury or surgery.
-
Treatment options for hypertrophic scars may include silicone gel or sheeting, pressure dressings, corticosteroid injections, laser therapy, and cryotherapy. These treatments are aimed at reducing the thickness and redness of the scar.
It is important to note that both keloids and hypertrophic scars can be challenging to treat, and the results can vary. A healthcare professional can evaluate the type and severity of the scar and recommend the most appropriate treatment options for each individual.
Prevention is an essential aspect of scar management, particularly in those who are at higher risk of developing hypertrophic or keloid scars. Here are some tips for scar prevention:
-
Early wound care: Proper wound care can help prevent the formation of scars. Clean the wound promptly, cover it with a sterile bandage or dressing, and keep it clean and dry until it heals.
-
Avoid scratching or picking at scabs: Scabs are a natural part of the healing process and help to protect the wound from infection. Avoid scratching or picking at scabs, as this can cause further injury to the skin and increase the risk of scarring.
-
Protect the wound from the sun: Exposure to the sun can cause discolouration and make scars more noticeable. Cover the wound with clothing or a bandage and use broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 to protect the area from the sun.
-
Avoid smoking: Smoking can slow down the healing process and increase the risk of scarring. Avoid smoking or using any tobacco products, particularly during the healing phase.
-
Treat scars promptly: Early treatment of scars can prevent them from becoming more noticeable and difficult to treat. Consult with a healthcare professional for advice on the best treatment options for your scar.
By following these prevention tips, you can help minimize the risk of developing hypertrophic or keloid scars and improve the overall appearance of your skin after an injury or surgery.
More detail about SHEEN CLINIC SDN BHD
 Malaysia
Malaysia