详情
【SUMMARY】
The HBsAg Rapid Test (Serum/Plasma) is a rapid test to qualitatively detect the presence of HBsAg in serum or plasma specimen. The test utilizes a combination of monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies to selectively detect elevated levels of HBsAg in serum or plasma. Viral hepatitis is a systemic disease primarily involving the liver. Most cases of acute viral hepatitis are caused by Hepatitis A virus, Hepatitis B virus (HBV) or Hepatitis C virus. The complex antigen found on the surface of HBV is called HBsAg. Previous designations included the Australia or Au antigen. 1 The presence of HBsAg in serum or plasma is an indication of an active Hepatitis B infection, either acute or chronic. In a typical Hepatitis B infection, HBsAg will be detected 2 to 4 weeks before the ALT level becomes abnormal and 3 to 5 weeks before symptoms or jaundice develop. HBsAg has four principal subtypes: adw, ayw, adr and ayr. Because of antigenic heterogeneity of the determinant, there are 10 major serotypes of Hepatitis B virus.
The HCV Rapid Test (Serum/Plasma) is a rapid test to qualitatively detect the presence of antibody to HCV in a serum or plasma specimen. The test utilizes colloid gold conjugate and recombinant HCV proteins to selectively detect antibody to HCV in serum or plasma. The recombinant HCV proteins used in the test kit are encoded by the genes for both structural (nucleocapsid) and non-structural proteins. Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) is a small, enveloped, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA Virus. HCV is now known to be the major cause of parenterally transmitted non-A, non-B hepatitis. Antibody to HCV is found in over 80% of patients with well- documented non-A, non-B hepatitis. Conventional methods fail to isolate the virus in cell culture or visualize it by electron microscope. Cloning the viral genome has made it possible to develop serologic assays that use recombinant antigens. 2,3 Compared to the first generation HCV EIAs using single recombinant antigen, multiple antigens using recombinant protein and/or synthetic peptides have been added in new serologic tests to avoid nonspecific cross-reactivity and to increase the sensitivity of the HCV antibody tests.
The HIV 1.2 Rapid Test (Serum/Plasma) is a rapid test to qualitatively detect the presence of antibody to HIV 1 and/or HIV 2 in serum or plasma specimen. The test utilizes latex conjugate and multiple recombinant HIV proteins to selectively detect antibodies to the HIV 1.2 in serum or plasma. HIV is the etiologic agent of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS). The virion is surrounded by a lipid envelope that is derived from host cell membrane. Several viral glycoproteins are on the envelope. Each virus contains two copies of positive-sense genomic RNAs. HIV 1 has been isolated from patients with AIDS and AIDS-related complex, and from healthy people with high potential risk for developing AIDS. 6 HIV 2 has been isolated from West African AIDS patients and from seropositive asymptomatic individuals. 7 Both HIV 1 and HIV 2 elicit immune response. 8 Detection of HIV antibodies in serum, plasma is the most efficient and common way to determine whether an individual has been exposed to HIV and to screen blood and blood products for HIV. 9 Despite the differences in their biological characteristics, serological activities and genome sequences, HIV 1 and HIV 2 show strong antigenic cross-reactivity. 10,11 Most HIV 2 positive sera can be identified by using HIV 1 based serological tests.
The Syphilis Rapid Test (Serum/Plasma) utilizes a double antigen combination of a Syphilis antigen coated particle and Syphilis antigen immobilized on membrane to detect TP antibodies (IgG and IgM) qualitatively and selectively in serum or plasma. Treponema Pallidum (TP) is the causative agent of the venereal disease Syphilis. TP is a spirochete bacterium with an outer envelope and a cytoplasmic membrane. 12 Relatively little is known about the organism in comparison with other bacterial pathogens. According to the Center for Disease Control (CDC), the number of cases of Syphilis infection has markedly increased since 1985. 13 Some key factors that have contributed to this rise include the crack cocaine epidemic and the high incidence of prostitution among drug users. One study reported a substantial epidemiological correlation between the acquisition and transmission of the HIV virus and Syphilis. Multiple clinical stages and long periods of latent, asymptomatic infection are characteristic of Syphilis. Primary Syphilis is defined by the presence of a chancre at the site of inoculation. The antibodies response to the TP bacterium can be detected within 4 to 7 days after the chancre appears. The infection remains detectable until the patient receives adequate treatment.
【DIRECTIONS FOR USE 】
Allow test cassette, specimen, bufferand/or controls to equilibrate to room temperature (15-30 °C) prior to testing.
1. Bring the pouch to room temperature before opening it. Remove the test cassette from the sealed pouch and use it as soon as possible. Best results will be obtained if the assay is performed within one hour.
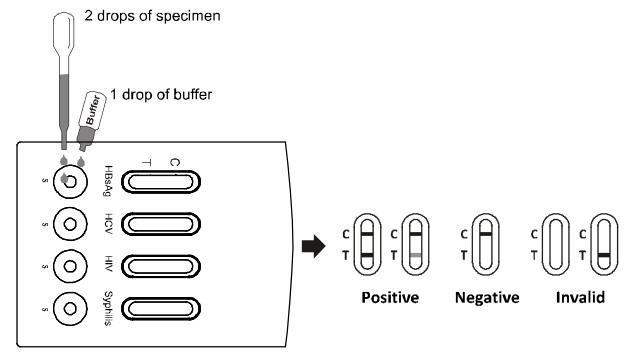
2. Place the test cassette on a clean and level surface. Hold the dropper vertically and transfer 2 drops of serum or plasma (approximately 50 ul) to the specimen well, then add 1 drop of buffer (approximately 40 m mL), respectively. Start the timer. See the illustration below.
3. Wait for the colored line(s) to appear. The test result should be read at 10 minutes. Do not interpret the result after 20 minutes.
Note: It is suggested not to use the buffer, beyond 30 days after opening the vial.
|
Cat. No. |
Product Description |
Specimen |
Format |
Kit Size |
Cut-Off |
Status |
|
IMID-345 |
HBsAg /HCV /HIV /Syphilis Combo Rapid Test Cassette |
S / P |
Cassette |
25 T |
See Insert |
Non-CE |
更多 Setia Scientific Solution 相关资料

 Malaysia
Malaysia