Laser Cutting In the world of metal fabrication, choosing the right cutting method for a project is crucial. Two of the most popular cutting technologies today are laser cutting and water jet cutting. Each method has its own set of strengths and weaknesses depending on the material, thickness, precision, and the complexity of the cut. Whether you're working in manufacturing, aerospace, automotive, or any other industry, understanding the differences between these two cutting methods can help you make an informed decision for your next project.
In this article, we will compare laser cutting and water jet cutting, exploring their pros and cons, applications, cost-effectiveness, and more. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a clearer idea of which method is best suited for your metal fabrication needs.
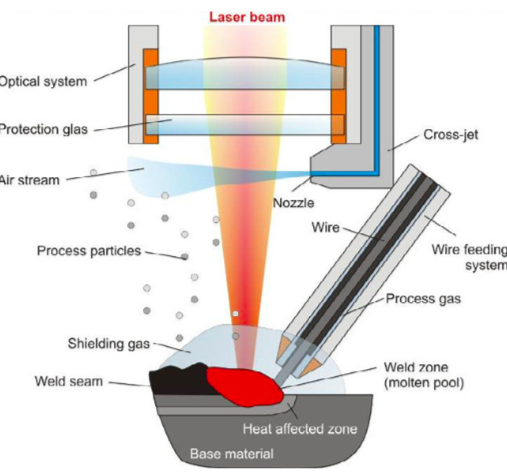
Laser cutting uses a focused laser beam to melt, burn, or vaporize material. The laser is directed at the surface of the material with high precision, making it capable of cutting through even thick metals. The process is widely used for cutting steel, stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and other metals, as well as non-metallic materials. The process is using a high-powered laser is focused on the material through a series of mirrors and lenses to do the cutting. The laser energy melts or vaporizes the material, and a gas jet (typically nitrogen or oxygen) helps blow away the molten material.The laser moves along a predefined path (controlled by CNC or computer numerical control), creating a clean, precise cut.

Water jet cutting uses high-pressure water (sometimes mixed with abrasives) to cut through materials. The water jet is typically capable of cutting through metal, stone, ceramics, and glass. The advantage of water jet cutting is that it does not create heat-affected zones (HAZ), making it suitable for materials sensitive to thermal changes. The cutting is by water which is pressurized to 50,000 psi or higher, and then forced through a fine nozzle to create a high-speed stream of water. The abrasive particles such as garnet are sometimes added to the water stream for cutting harder materials. The CNC system controls the path of the water jet to create precise cuts.
To help you decide which cutting method best suits your fabrication project, let's break down the key aspects of laser cutting and water jet cutting in terms of their precision, cost, material compatibility, speed, and applications.
Summary: Both methods offer excellent precision, but laser cutting is slightly better for intricate cuts and fine details. Water jet cutting is ideal for thicker or sensitive materials where heat distortion is a concern.
Summary: Water jet cutting has an advantage in material compatibility due to its ability to cut through a broader range of materials, including thicker or more sensitive ones. Laser cutting excels with metals, especially thinner materials.
Summary: Laser cutting is generally faster than water jet cutting for thin materials, while water jet cutting may be slower but can handle thicker materials without compromising quality.
Summary: Water jet cutting has a clear advantage in applications where heat distortion must be avoided, while laser cutting may still be acceptable for materials that can tolerate minor heat effects.
Summary: Laser cutting is often more cost-effective for high-volume production of thin materials, while water jet cutting might incur higher operating costs, especially for thicker or specialized materials.
Choosing between laser cutting and water jet cutting depends largely on your specific metal fabrication needs. Here’s a quick guide:
Go for laser cutting if:
Go for water jet cutting if:
Both laser cutting and water jet cutting have distinct advantages, making them suitable for different applications. Laser cutting excels in terms of precision, speed, and cost-efficiency for thin materials, while water jet cutting offers greater versatility for a wide range of materials, especially thicker and heat-sensitive materials. Ultimately, the best choice will depend on factors such as the material you are working with, your desired cutting speed, the cut quality required, and your project’s budget.
Understanding these differences will help you choose the best cutting method that aligns with your fabrication goals, whether you prioritize cost-effectiveness, precision, or material compatibility.
 Japan
Japan