Enterprise Security Management
1. What server hosting options are available for the Security Management System (SMS)?
The SMS server can be hosted by an on-premise server for maximum security and local control. This option is suited to organisations with in-house IT support and isolated security LAN. On-premise hosting can be via a physical server or a VM to fully optimise on corporate shared IT resources. Increasingly corporates are outsourcing such hosting services to data centres. In such cases, the option to host the SMS in a cloud server is ideal.
2. How can a Security Management System (SMS) survive a server failure?
There are many parts of any server hardware that can fail. For example, the CPU can overheat, or the hard disk drives can crash, etc. In order for the SMS to survive a server failure due such hardware fault, the Server Failover module is required. The Server Failover is a software module that performs periodic functions such as database replication, heart-beat monitoring and automatic switchover from a primary server to the secondary server, just to name a few. Upon failure of the primary server, the secondary server is immediately activated and takes over control of all the key services. The secondary assumes the role of the primary and re-establishes all connections with the access controllers and operator workstations so that the entire system continues to operate as normal.
3. How can a Security Management System (SMS) handle multiple locations?
A corporate with multiple functions or branches with a centrally hosted server can delegate operational responsibility to each function/branch with the Security Area (SA) module. Each area (function/branch) may be defined to operate as a virtual autonomous security centre with its administrator in complete control of the defined area. Key applications include corporates with a HQ and multiple branches/subsidiaries, as well as corporates with distributed functions (manufacturing, warehouse, workshop, retail, etc.).
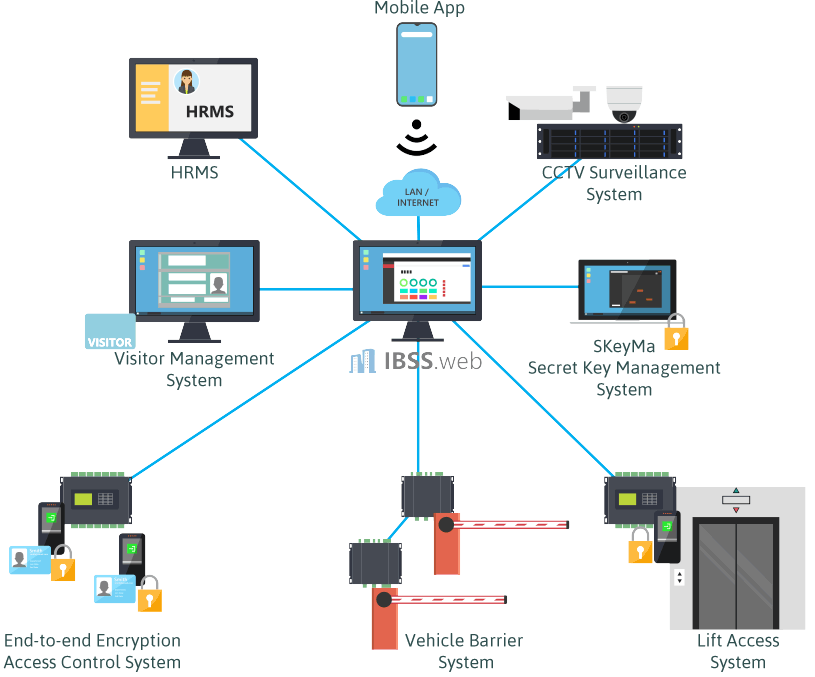
4. How can the Security Management System (SMS) integrate with SAP or other HR systems?
The HR Database Integrator (HRDI) module facilitates the synchronization of employee data in most human resource management system (HRMS) with the IBSS.web, so that any change in employee data made in the HRMS is seamlessly registered to the IBSS.web database. When any employee data is received from the HRMS, the HRDI automatically assigns predefined access rights to new employees according to its HR policy and/or removes the access rights of employees who have resigned. The HRDI will bring about significant productivity improvements with automation in managing employee movements and payroll administration. Operational efficiency is enhanced with significant improvements in productivity.
5. How to ensure login access is automatically disabled when a user resigns?
The Security Management System (SMS) supports Active Directory (AD) for Single Sign-on (SSO). When a staff logs on to his workstation, the system checks his online active directory and uses his credential to map the corresponding access rights in the SMS. When the rights of the staff in the active directory is removed upon resignation, all corresponding assigned rights including access to the SMS software is removed automatically.

System Architecture



 Malaysia
Malaysia