A server is a dedicated computer that provides services on behalf of clients, such as ordinary desktop computers or workstations.
As shown below Figure, it is a centralized machine where multiple clients connect, either over the internet or in a local area network, to access a specific service provided by the server.
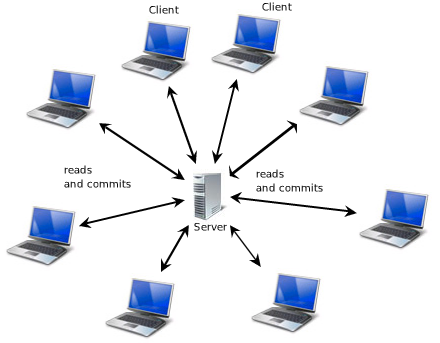
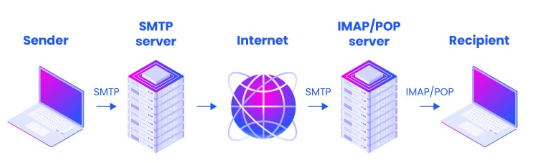
A server service could involve retrieving a website, accessing data, or handling email, as illustrated below Figure. In some cases, a server may be dedicated to a single service, such as one server for websites, another for data storage, and a separate server for email. This approach is commonly used by larger organizations. Alternatively, a server can be configured to manage multiple services on the same machine, a setup more typical of smaller organizations. The choice of setup depends on the specific needs of the organization.
When people refer to a server, they typically mean a powerful centralized computer that clients connect to over a network. While this is accurate, a server is not just a physical computer; it is a role that a computer takes on. Any ordinary desktop computer can be configured as a server, and it does not necessarily have to be a powerful machine. For example, in a home network, an ordinary desktop computer can serve as a file server by hosting files in a shared folder that other computers can access. Similarly, a desktop computer can function as a web server by hosting website data and allowing other computers to connect and retrieve web pages.
However, desktop computers have limitations in handling large workloads and numerous incoming connections due to their hardware and software constraints. Desktop operating systems are designed to manage a limited number of concurrent connections. Servers need to operate 24/7, as they are crucial to an organization, and any downtime could jeopardize business operations. Therefore, servers require reliable hardware capable of continuous operation with minimal downtime. For instance, desktops typically use processors designed for consumer use, such as Intel Core series processors, while servers use processors designed for high performance and reliability, such as Intel Xeon processors, as shown below Figure.
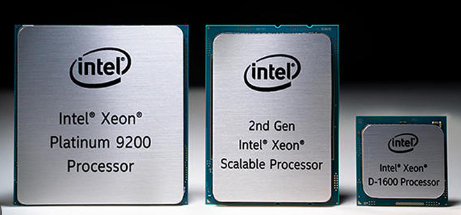
A server processor needs to be fast and capable of performing numerous tasks simultaneously. As shown above Figure, these processors are powerful but differ in several ways. For instance, Xeon processors support a multi-processing environment, allowing multiple processors to work together on a server motherboard. This capability is essential for handling large workloads, which is common in server environments. In contrast, desktop processors are designed to operate independently and do not support multi-processing configurations.
A server should also have hot-swappable hard drives in a RAID configuration. If a hard drive fails, there will be no data loss, and the server will remain operational due to RAID. RAID copies data across multiple disks, allowing for data redundancy. If a hard drive fails, it can be removed and replaced without shutting down the server, and RAID will automatically rebuild the data on the new hard drive.

A server should also have redundant power supplies to ensure continuous operation in case of a power supply failure, as shown in the above Figure. Additionally, a server needs to use a server operating system such as Linux, Windows Server, or Mac OS Server. These operating systems are robust and stable, designed for nonstop operation, and capable of handling thousands of concurrent connections.

What are the benefits of having a server?
Centralized Data Management: All data is stored in one location, making it easier to manage, backup, and secure.
Resource Sharing: Servers allow multiple users to share resources such as files, printers, and applications.
Enhanced Security: Servers offer robust security features, including access controls, encryption, and regular updates, to protect data.
Improved Collaboration: Centralized servers enable better collaboration by allowing multiple users to access and work on the same files simultaneously.
Scalability: Servers can be scaled up or down based on the needs of the organization, accommodating growth or reduction in demand.
Remote Access: Users can access the server and its resources from anywhere, facilitating remote work and business continuity.
Reliability and Uptime: Servers are designed for high reliability and uptime, ensuring that services and applications are available when needed.
Performance: Servers are optimized for handling multiple requests simultaneously, providing better performance than regular computers.
Centralized Software Management: Easier to deploy, update, and manage software across all connected devices.
Backup and Recovery: Servers typically have robust backup solutions, reducing the risk of data loss and ensuring quick recovery in case of a disaster.
Cost-Effective in the Long Run: While the initial investment may be high, servers can reduce costs in the long run through centralized management and resource sharing.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of server?
Advantages
Centralized Data Management:
Efficiently manage, back up, and secure data from a single location.
Resource Sharing:
Enables multiple users to share resources like files, printers, and applications.
Enhanced Security:
Provides robust security features such as access controls, encryption, and regular updates.
Scalability:
Easily scale up or down to meet the organization’s needs.
Remote Access:
Enables users to access the server and its resources from anywhere, supporting remote work.
Reliability and Uptime:
Designed for high reliability and uptime, ensuring services and applications are always available.
Performance:
Optimized for handling multiple requests simultaneously, offering better performance than regular computers.
Disadvantages
High Initial Cost:
The initial setup cost for servers, including hardware, software, and network infrastructure, can be high.
Maintenance and Management:
Requires regular maintenance and skilled personnel to manage and troubleshoot issues.
Complexity:
Setting up and managing a server environment can be complex and may require specialized knowledge.
Dependence on Network:
Servers are dependent on network connectivity; any network issues can impact access to server resources.
Security Risks:
Servers can be targets for cyberattacks, requiring robust security measures and constant monitoring.
Single Point of Failure:
Despite redundancy measures, if a critical server component fails without backup, it can disrupt business operations.
Energy Consumption:
Servers consume significant amounts of power, leading to higher energy costs.
Space Requirements:
Servers require dedicated physical space, often with cooling and other environmental controls.
Are Servers Essential for Modern IT infrastructure?
Yes, different types of servers are essential for running, managing, and maintaining IT infrastructure. Here's how each type contributes to the IT landscape.
A Professional Diploma in IT Support can be valuable in the IT world, but in different capacities.
Diploma in IT Support
Foundation in IT Infrastructure:
IT support diplomas typically provide a strong foundation in understanding and troubleshooting computer systems, networks, and hardware. This knowledge is essential for maintaining the servers that support various IT systems.
System Administration:
IT support programs often cover aspects of system administration, including configuring servers, managing databases, and ensuring the smooth operation of IT environments. These skills are crucial for setting up and maintaining the servers needed to run applications and services.
Troubleshooting and Technical Support:
IT support diplomas equip students with skills in diagnosing and resolving technical issues, which is invaluable in settings where server hardware, software, or network problems can impact system performance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, IT support plays indispensable roles in maintaining and optimizing IT infrastructure. Different types of servers play indispensable roles in IT infrastructure. Server management and IT support form a synergistic partnership in the IT landscape. While IT support ensures the smooth operation and maintenance of servers, server managers optimize and secure server technologies that drive business operations and enhance efficiency.

 Malaysia
Malaysia