Overview of IBS
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a common gastrointestinal disorder characterized by a group of symptoms that impact intestinal health. These symptoms often include constipation, diarrhea, stomach bloating, excessive gas, and stomach discomfort or pain.
.jpg)
Types of IBS
IBS can be categorized into three main types based on the predominant symptoms:
| IBS-C | IBS-D | IBS-M |
.png) |
 |
 |
| Constipation, with hard, lumpy stools | Diarrhea, with loose or watery stools | Mix of both constipation and diarrhea |
The differences are important as certain treatments only work for specific types of IBS.
Signs and Symptoms
You don’t always experience symptoms. On some days, symptoms may ease, and your bowel movements will be normal. However, there are times when symptoms like the following may return:
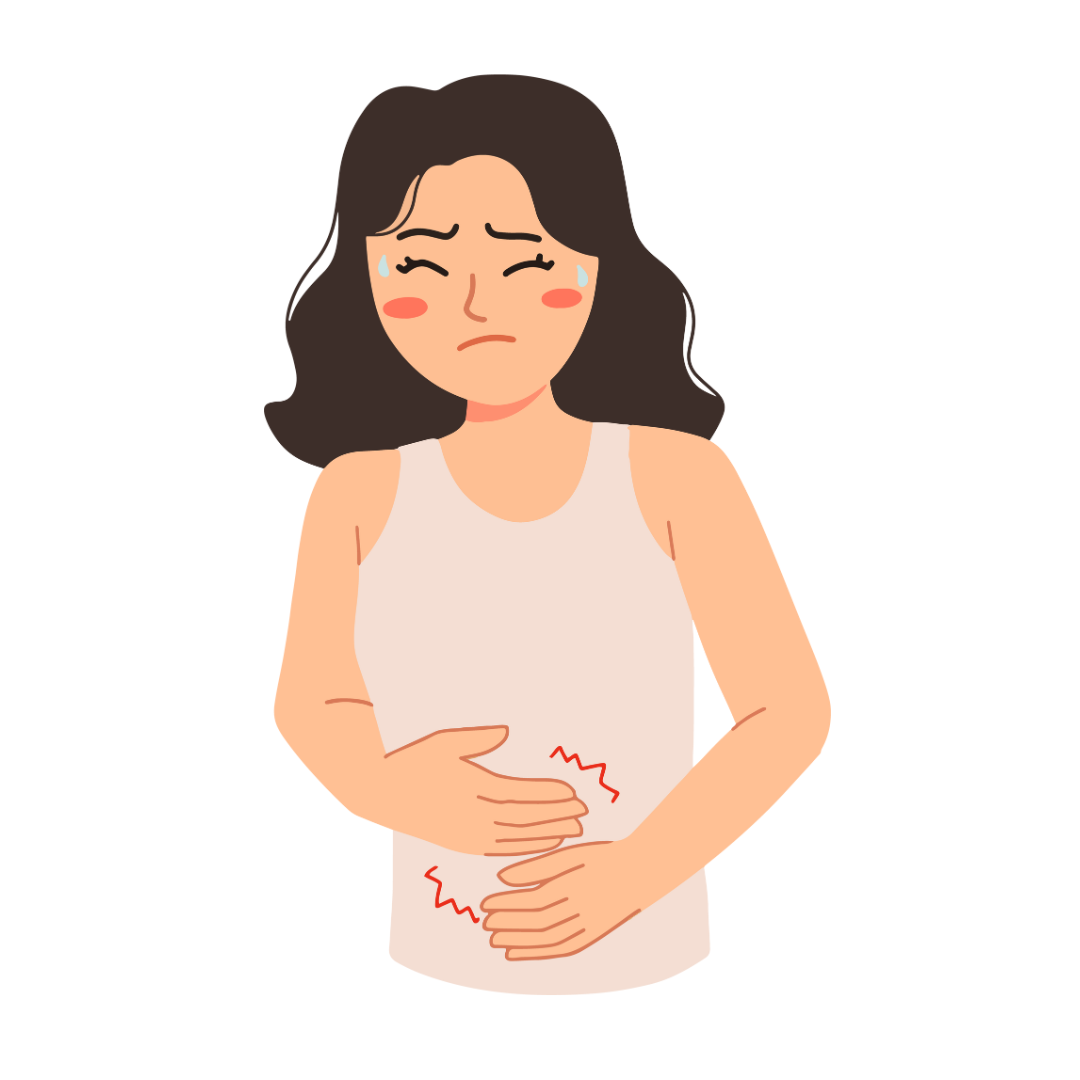




Causes of IBS
Several factors may contribute to IBS, including:
.jpg) |
• Gut-brain interaction disorder: Miscommunication between the brain and gut can cause the body to overreact to normal changes in the digestive process. |
.jpg) |
• Altered Gut Microbiota: Imbalance in gut bacteria may trigger or worsen symptoms. |
.jpg) |
• Food Intolerance: Certain foods can trigger IBS symptoms, such as dairy, fatty foods, caffeine, alcohol, and food high in FODMAPs (fermentable carbohydrate). |
.jpg) |
• Stress: Psychological stress and anxiety can worsen IBS symptoms. |
.jpg) |
• Infections: IBS can occur after a severe gastrointestinal infection. |
Diet and Lifestyle Tips
Managing IBS often involves personalized dietary and lifestyle adjustments:
.jpg) |
1. Drinks 6 to 8 glasses of water daily: Adequate hydration is crucial for proper digestion. |
.jpg) |
2. Do not skip meals: It can disrupt the natural rhythm of your digestive system. |
.jpg) |
3. Exercise regularly: At least 150 mins/week, it is a great way to ease stress and can also help ease constipation. |
.jpg) |
4. Reduce coffee and caffeine drinks: Caffeine can stimulate the muscles in the colon and increase diarrhea. |
.jpg) |
5. Don’t drink alcohol: It can irritate your digestive tract. |
.png) |
6. Avoid Trigger Foods: Limit fatty, oily, spicy, and caffeinated foods. |
.jpg) |
7. Take probiotics: Kill bad bacteria in gut and improve gut health. |
.jpg) |
8. Increase Fiber Gradually: Increase soluble fiber (like oats) to help with constipation, and reduce insoluble fiber (like whole grains) if bloating worsens. |
.jpg) |
9. Eating a low-FODMAP diet: Reducing foods that are high in fermentable carbohydrates like onion, garlic and brown rice as your body cannot digest it well. |
IBS may be a lifelong condition, but with the right approach, its symptoms can be effectively managed.

 Singapore
Singapore